Taxes and Fees
Real estate-related taxes and fees in Japan
■Descriptions of real estate-related taxes in Japan
■Descriptions of real estate-related fees in Japan
Descriptions of real estate-related taxes in Japan
Statutory effective tax rate for rental income
When a corporation earns income from renting its real estate property, the rental income is included in the total amount of income subject to corporate tax, resident tax, and business tax. Thus corporate and other taxes are imposed on its rental income at approximately 30%, the statutory effective tax rate.
The capital gains tax is imposed on gains from sales of real estate such as lands and buildings. In the case of an individual, real estate income is calculated apart from other income calculations. If the holding period of a property is five years or less, income tax of 30% and resident tax of 9% are imposed as a capital gains tax on the transfer of real estate. If the holding period of a property is more than five years, income tax of 15% and resident tax of 5% are imposed as a capital gains tax on the transfer of real estate. In the case of a corporation, the gain is included in taxable revenue to calculate the total amount of taxable income to determine the amount of corporate tax, for which an effective corporate tax rate of approximately 30% is applied.
Property tax and city planning tax
Property tax and city planning tax, imposed on owners of fixed assets such as land and buildings on January 1 of each year, are paid to the local municipalities where the assets are located. Amounts are calculated based on the value of the assets. The standard rate of property tax is 1.4% and the rate of city planning tax is 0.3% (in Tokyo 23ward).
A real estate acquisition tax is imposed only once when real estate such as land and buildings is acquired. Acquisition of real estate is defined as acquisition of ownership of real estate through transactions such as buying and selling, donations, exchanges, and construction (for new buildings, extensions, or alterations). If real estate is acquired by inheritance, this tax need not be paid. A standard rate of 4% (although special provisions present 3% for land and housing [up to March 31, 2027] and 4% for buildings other than housing) is applied against the real estate value.
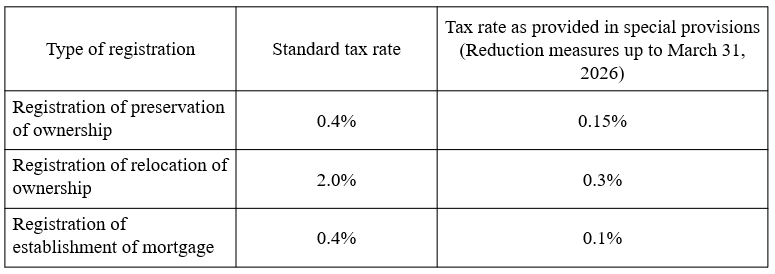
When land and buildings are constructed or bought, registration and license taxes are imposed mainly for registration of preservation and relocation of ownership. The following tax rates are imposed against the real estate value for registration and license taxes.
A consumption tax is imposed on transactions such as the sale of goods and the supply of services in Japan. The consumption tax rate was raised to 10% on October 1, 2019. Whereas specific real estate transactions are subject to the consumption tax, others are not, as shown below.
[Subject to consumption tax]
-Purchase price of buildings, construction sales price
-Brokerage commissions (for sales and leasing)
-Housing loan administration fees
-Rent for offices, stores, etc.
-Judicial scrivener fees, registered land and building investigator fees
[Not Subject to consumption tax]
-Purchase price of land
-Interest and guarantee fee for housing loan
-Fire and life insurance premiums
-Land rent, residential rent
-Security deposits, tenant leaseholds
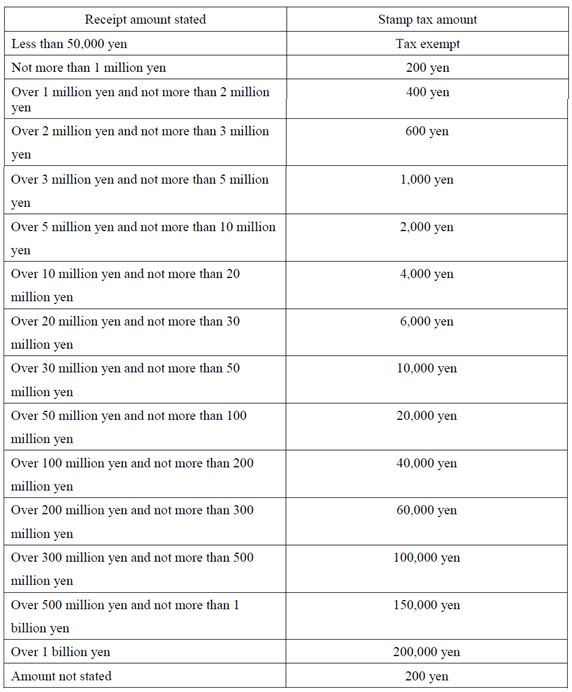
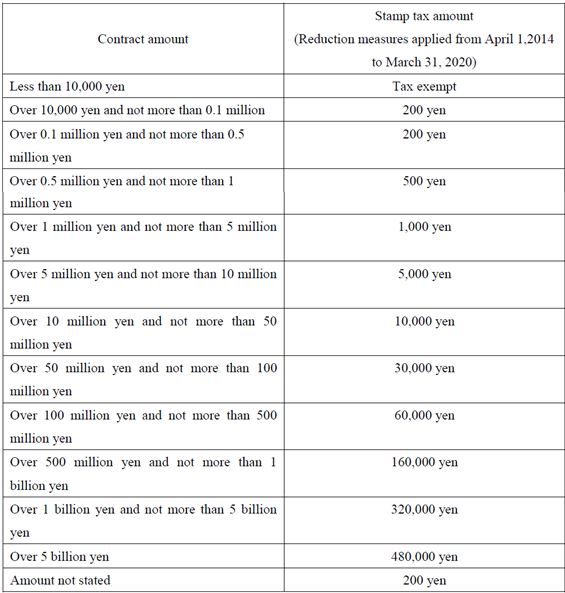
When documents such as contracts and receipts are prepared, revenue stamps are required to be purchased and pasted on the documents and then postmarks need to be stamped on them. The following are the amounts of stamp tax required for documents related to real estate transactions.
[Receipts, etc. (for example, real estate rent receipt)]
[Sales contract of real estate]
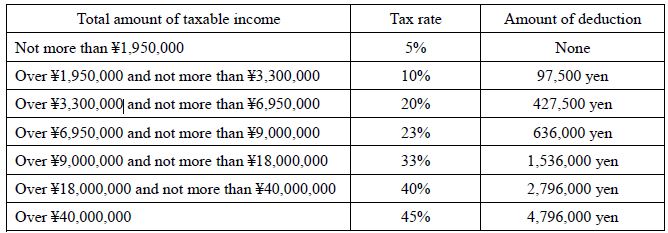
Gift tax is imposed on the recipient of gifted assets. In cases where real estate such as land and buildings is obtained free of charge, and cases where the purchase money for real estate is donated, payment of the gift tax is required.
The amount of gift tax is calculated as follows:
Taxable amount=Gifted asset value-1,100,000 yen (basic deduction)
Tax amount=Taxable amount × Tax rate-Amount of deduction
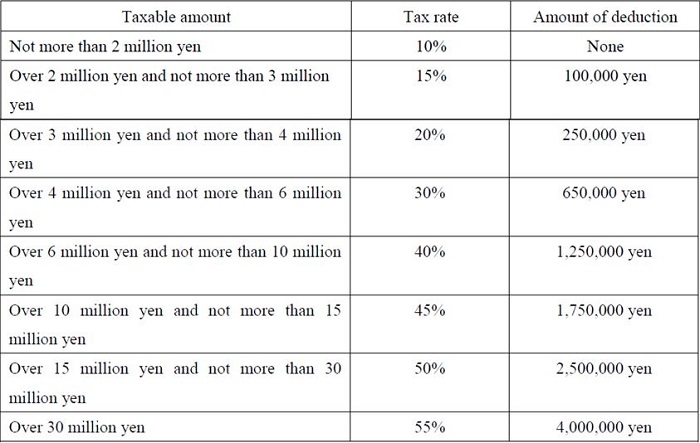
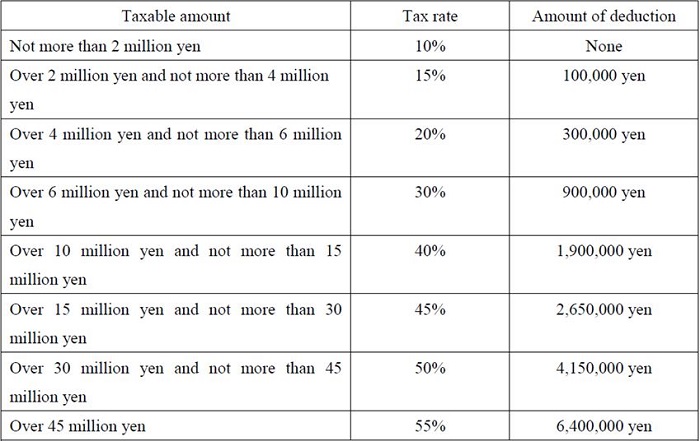
The tax rate for gift tax has been changed to the following rate since January 1, 2015 because of a tax reform.
[Ordinary case of donation]
[Special case of donation to a child or a grandchild of the age of 20 years or over from the parents or grandparents]
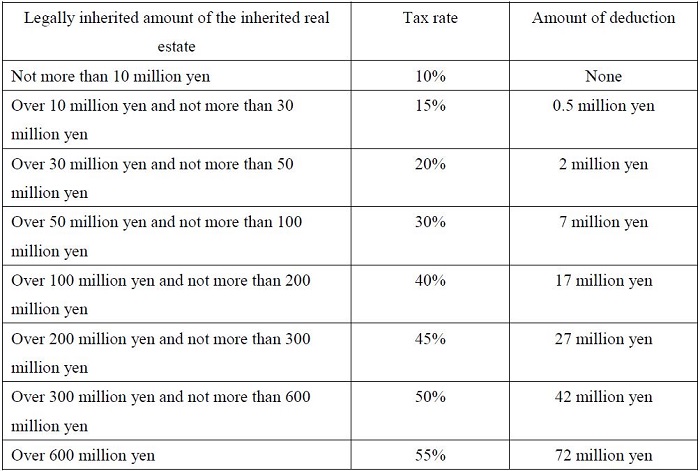
Inheritance tax is imposed when real estate such as land and buildings is acquired through inheritance. The taxable amount of total inheritance subject to the inheritance tax is calculated by deducting the basic deduction amount etc. from the total amount of inheritance. The basic deduction amount has been changed to the following since January 1, 2015 because of a tax reform.
Basic deduction amount=30 million yen+6 million yen×number of successors by law
The legally inherited amount out of the taxable amount of total inheritance for each successor is determined according to law, and the tax rate is applied to calculate the tax amount for each successor by law.
The tax rate for inheritance tax is as follows:
Descriptions of real estate-related fees in Japan
Real estate broker commissions
[Sales of real estate]
When a real estate transaction is concluded, a brokerage commission is required to be paid to the broker. The amount of this commission, whose upper limit is regulated by the Building Lots and Buildings Transaction Business Act, can be decided by the real estate company on its own as long as it does not exceed the limit.
The upper limit of commissions for sales contracts is 3% of the sales price +60,000 yen + tax (10%), only for the case that the property price is more than 4,000,000yen.
Half of the brokerage commission for a sales contract is generally paid when the contract is entered into. The other half is paid when the payment is settled and the property delivered.
[Leasing of real estate]
The total amount of commissions received from both clients (lessor and lessee) is equivalent to the sum of monthly amount of rent and consumption tax.
Without any unified standard, judicial scrivener fees are freely determined and the amount differs materially depending upon the judicial scrivener.
Apart from other income, income earned by real estate sales is subject to income tax and resident tax. The income earned by sales is calculated by deducting acquisition expenses and sales expenses from the total amount earned by real estate sales. Acquisition expenses are expenses arising from the acquisition of the real estate and sales expenses include brokerage commissions paid to real estate companies, revenue stamp fees for sales contracts, and costs of surveying.
Total amount of expenses concerning real estate purchase and sales
Apart from other income, income earned by real estate sales is subject to income tax and resident tax. The income earned by sales is calculated by deducting acquisition expenses and sales expenses from the total amount earned by real estate sales. Acquisition expenses are expenses arising from the acquisition of the real estate and sales expenses include brokerage commissions paid to real estate companies, revenue stamp fees for sales contracts, and costs of surveying.
Taxes and fees concerning rent
Apart from other income, income earned by real estate sales is subject to income tax and resident tax. The income earned by sales is calculated by deducting acquisition expenses and sales expenses from the total amount earned by real estate sales. Acquisition expenses are expenses arising from the acquisition of the real estate and sales expenses include brokerage commissions paid to real estate companies, revenue stamp fees for sales contracts, and costs of surveying.